TOR in a nutshell
In the mid-nineties, the US Navy devised a concept called “onion routing”, as a way that the Navy could ensure secure communication when trying to transfer sensitive intelligence.

It was further developed in the late nineties by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and released in 2002.
By 2006, The Tor Project had been founded - a Massachusetts-based 501(c)(3) research-education nonprofit organization responsible for maintaining Tor.
At its absolute most basic level, Tor uses its network of volunteers to create relays for internet traffic that allow for user anonymity.
How does Tor work?
To understand how Tor works, you need to understand a little bit about how the internet works.
Usually, when you connect to the internet with a web browser, not only are you accessing ‘packets’ of information (like apps, websites, etc.), but you are also sending out packets of information about yourself (IP address, browser, device fingerprint).
The Tor network is accessed through its browser (based on the Firefox codebase), and it strips all of your packets. The browser then bounces your information to the various nodes, encrypting your data at every layer.
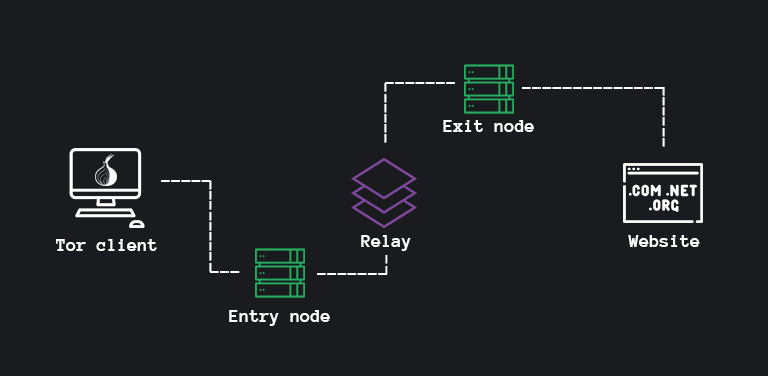
Think of Tor as an anonymity onion.
You go through the onion and hit an “exit node” before you’ve even gone to a website. The Tor network bounces around the location of a user, essentially rendering it impossible to track.
How do I use Tor?
While all of that might sound complicated, at the user end, Tor is simply a web browser that you would use like Safari, Chrome, or Firefox.
Download the browser from the official website, and it will establish necessary connection details for you.
Once you hit connect, it may take a few minutes to connect you through the relays, but from there it will work just like a standard browser.
You will also gain access to .onion domains, which are not accessible thought regular browsers.
Take-Aways
While Tor has become synonymous with the idea of accessing the ‘dark web’, or illegal activity, the truth is that people do all of those actions once they’ve entered the network.
The browser itself is simple and easy to use and is not at all illegal.
So if you’re concerned about your anonymity, Tor might be the perfect choice for you.
